Operation View
Business Partner KIT
Local Deployment
BPDM is an acronym for business partner data management. This project provides core services for querying, adding and changing business partner base information in the Eclipse Tractus-X landscape. BPDM project is SpringBoot Kotlin software project managed by Maven and consists of three microservices. This section contains information on how to configure and run the BPDM application.
This local deployment is an easy installation with helm. This setup is built to run on a kubernetes cluster.
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Install the prerequisites | Install all necessary tools for this setup | |
| Check out the Code | Get all necessary code to deploy the service and dependencies to the kuberneetes cluster | |
| Installing the Service | Start cluster and interact with Services |
Step 1: Prerequisites
Docker is installed and the Docker deamon is running with at least 8GB of memory
helm is installed
Minikube is installed and running.
You can also use any other local Kubernetes cluster, this guide is just using Minikube as a reference.minikube start --memory 8192 --cpus 2Optional: enable minikube metrics
minikube addons enable metrics-serverkubectl is installed
psql client is installed
Step 2: Check out the code
Check out the project BPDM or download a released version of the project.
Step 3: Installing the services
1. Start the cluster
To deploy the services on kubernetes using helm charts, run
cd local/bpdm
helm install your_namespace ./charts/bpdm/
If postgresql is not available in your cluster then you might get following error.
Error: INSTALLATION FAILED: An error occurred while checking for chart dependencies. You may need to run `helm dependency build` to fetch missing dependencies: found in Chart.yaml, but missing in charts/ directory: opensearch, postgresql
You can resolve it by adding dependancy to the build
helm dependency build ./charts/bpdm/
This can take up to 5 minutes.
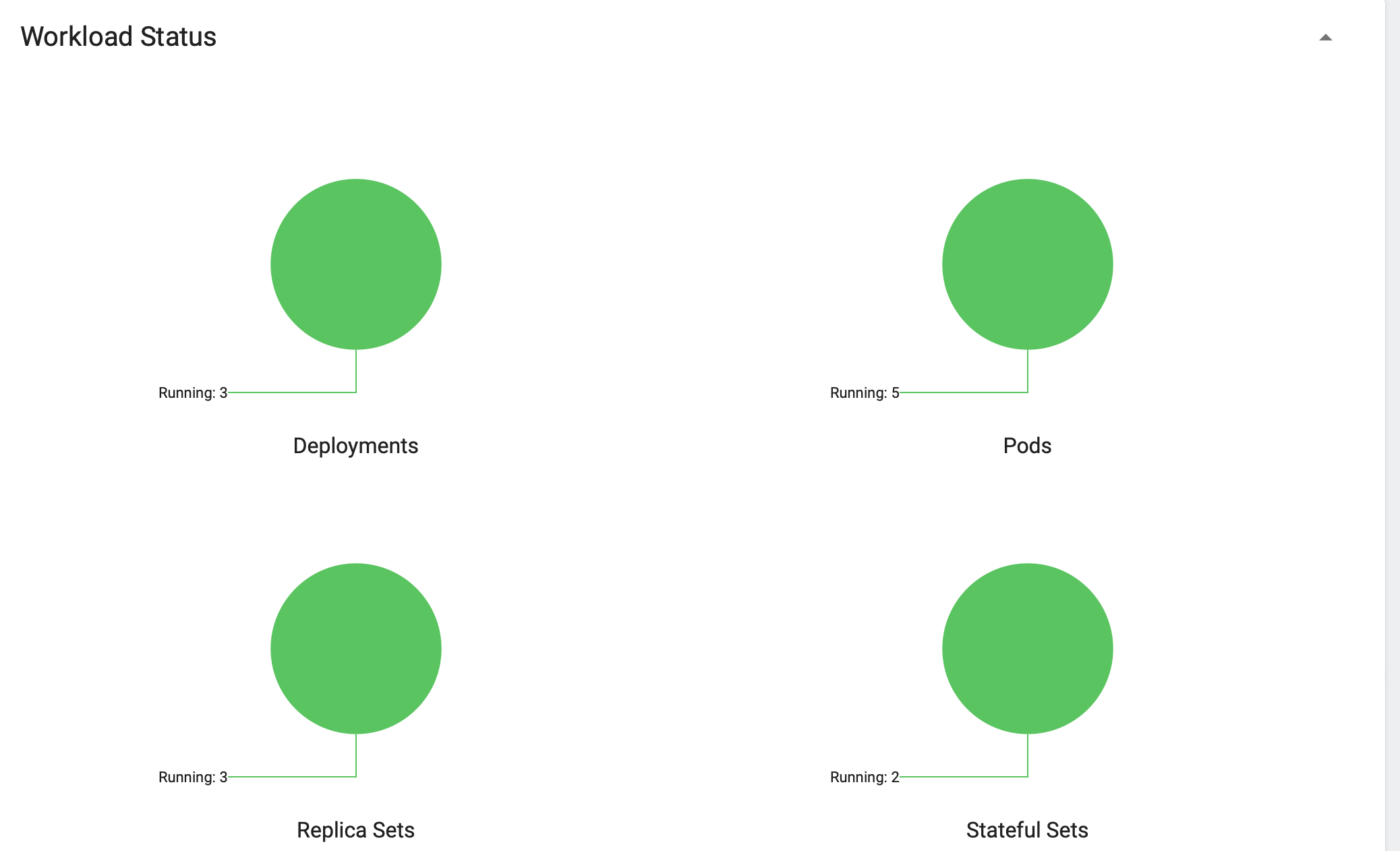
When the deployment is finished you can expect that 3 deployments can be seen in the minikube dashboard:
- bpdm-bridge-dummy
- bpdm-gate
- bpdm-pool
- bpdm-cleaning-dummy
- bpdm-orchestrator
Also in total 5 Pods are up and running.
1.1 Get the status of the deployment
The minikube dashboard will give you feedback on how the status of the deployment currently is:
minikube dashboard
Make sure you select the namespace your_namespace:
2. Forward ports
When the deployment has been finished, you can for port forwarding using k9s. Also, if k9s tool is not installed the you can use installer
<shift+f>
or port forwarding can also be achived kubernetes command
kubectl port-forward <pod-name> <locahost-port>:<pod-port>
After that you can access the:
- bpdm-bridge-dummy: http://localhost:8083
- bpdm-gate: http://localhost:8081
- bpdm-pool: http://localhost:8080
Deploy Individual Service
1. BPDM Pool
The prerequisites for running this service. In an existing Kubernetes cluster the application can be deployed with the following command:
helm install release_name ./charts/bpdm/bpdm-pool --namespace your_namespace
This will install a new release of the BPDM Pool in the given namespace.On default values this release deploys the latest image tagged as main from the repository's GitHub Container Registry. The application is run on default profile (without authorization).
Additionally, the Helm deployment contains a PostgreSQL database and Opensearch instance which the BPDM Pool connects to.
On the default values deployment no further action is needed to make the BPDM Pool deployment run. However, per default, ingress as well as authentication for endpoints are disabled.
By giving your own values file you can configure the Helm deployment of the BPDM Pool freely:
helm install release_name ./charts/bpdm/bpdm-pool --namespace your_namespace -f ./path/to/your/values.yaml
In the following sections you can have a look at the most important configuration options.
Image Tag
Per default, the Helm deployment references a certain BPDM Pool release version where the newest Helm release points to the newest Pool version. This is a stable tag pointing to a fixed release version of the BPDM Pool. For your deployment you might want to follow the latest application releases instead.
In your values file you can overwrite the default tag:
image:
tag: "latest"
Profiles
You can also activate Spring profiles in which the BPDM Pool should be run. In case you want to run the Pool with authorization enabled you can write the following:
springProfiles:
- auth
Ingress
You can specify your own ingress configuration for the Helm deployment to make the BPDM Pool available over Ingress. Note that you need to have the appropriate Ingress controller installed in your cluster first. For example, consider a Kubernetes cluster with an Ingress-Nginx installed. An Ingress configuration for the Pool deployment could look like this:
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTP"
hosts:
- host: business-partners.your-domain.net
paths:
- path: /pool
pathType: Prefix
Pool Configuration
The Helm deployment comes with the ability to configure the BPDM Pool application directly over the values file.
This way you are able to overwrite any configuration property of the application.properties and application-auth.properties files.
Consider that you would need to turn on auth profile first before overwriting any property in the corresponding properties file could take effect.
Overwriting configuration properties can be useful to connect to a remote service:
applicationConfig:
bpdm:
security:
auth-server-url: https://remote.keycloak.domain.com
realm: CUSTOM_REALM
client-id: POOL_CLIENT
In this example above a Pool with authenticated activated connects to a remote Keycloak instance and uses its custom realm and resource.
Entries in the "applicationConfig" value are written directly to a configMap that is part of the Helm deployment.
This can be a problem if you want to overwrite configuration properties with secrets.
Therefore, you can specify secret configuration values in a different Helm value applicationSecrets.
Content of this value is written in a Kubernetes secret instead.
If you want to specify a custom database password for example:
applicationSecrets:
spring:
datasource:
password: your_database_secret
Helm Dependencies
On default, the Helm deployment also contains a PostgreSQL and Opensearch deployment.
You can configure these deployments in your value file as well.
For this, consider the documentation of the correspondent dependency PostgreSQL
or Opensearch.
In case you want to use an already deployed database or Opensearch instance you can also disable the respective dependency and overwrite the default host
address in the applicationConfig:
applicationConfig:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:postgresql://remote.host.net:5432/bpdm
postgres:
enabled: false
2. BPDM Gate
The prerequisites for running this service is same except this service need running BPDM Pool instance.
In an existing Kubernetes cluster the application can be deployed with the following command:
helm install release_name ./charts/bpdm/bpdm-gate --namespace your_namespace -f /path/to/my_release-values.yaml
This will install a new release of the BPDM Gate in the given namespace.
On default values this release deploys the latest image tagged as main from the repository's GitHub Container Registry.
The application is run on default profile (without authorization for its own endpoints or BPDM Pool endpoints).
This deployment requires a BPDM Pool deployment to be reachable under host name bpdm-pool on port 8080.
By giving your own values file you can configure the Helm deployment of the BPDM Gate freely. In the following sections you can have a look at the most important configuration options.
Image Tag
Per default, the Helm deployment references the latest BPDM gate release tagged as main.
This tag follows the latest version of the Gate and contains the newest features and bug fixes.
You might want to switch to a more stable release tag instead for your deployment.
In your values file you can overwrite the default tag:
image:
tag: "latest"
Profiles
You can also activate Spring profiles in which the BPDM Gate should be run. In case you want to run the Gate with authorization and oAuth Pool client enabled you can write the following:
springProfiles:
- auth
- pool-auth
Ingress
You can specify your own ingress configuration for the Helm deployment to make the BPDM Gate available over Ingress. Note that you need to have the appropriate Ingress controller installed in your cluster first. For example, consider a Kubernetes cluster with an Ingress-Nginx installed. An Ingress configuration for the Gate deployment could look like this:
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTP"
hosts:
- host: business-partners.your-domain.net
paths:
- path: /companies/test-company
pathType: Prefix
Gate Configuration
For the default deployment you already need to overwrite the configuration properties of the application.
The Helm deployment comes with the ability to configure the BPDM Gate application directly over the values file.
This way you are able to overwrite any configuration property of the application.properties, application-auth.properties
and application-pool-auth.properties files.
Consider that you would need to turn on auth and pool-auth profile first before overwriting any property in the corresponding properties file could take
effect.
Overwriting configuration properties can be useful for connecting to a remotely hosted BPDM Pool instance:
applicationConfig:
bpdm:
pool:
base-url: http://remote.domain.net/api/catena
Entries in the "applicationConfig" value are written directly to a configMap that is part of the Helm deployment.
This can be a problem if you want to overwrite configuration properties with secrets.
Therefore, you can specify secret configuration values in a different Helm value applicationSecrets.
Content of this value is written in a Kubernetes secret instead.
If you want to specify a keycloak client secret for example:
applicationSecrets:
bpdm:
security:
credentials:
secret: your_client_secret
3. BPDM Bridge Dummy
The prerequisites for running this service is same. In an existing Kubernetes cluster the application can be deployed with the following command:
helm install release_name ./charts/bpdm/bpdm-bridge-dummy --namespace your_namespace -f /path/to/my_release-values.yaml
This will install a new release of the BPDM Bridge Dummy in the given namespace.
On default values this release deploys the latest image tagged as main from the repository's GitHub Container Registry.
By giving your own values file you can configure the Helm deployment of the BPDM Bridge Dummy freely. In the following sections you can have a look at the most important configuration options.
Image Tag
Per default, the Helm deployment references the latest BPDM Bridge Dummy release tagged as main.
This tag follows the latest version of the Bridge Dummy and contains the newest features and bug fixes.
You might want to switch to a more stable release tag instead for your deployment.
In your values file you can overwrite the default tag:
image:
tag: "latest"
Profiles
You can also activate Spring profiles in which the BPDM Bridge Dummy should be run. In case you want to run the Bridge Dummy with authorization enabled you can write the following:
springProfiles:
- auth
Ingress
You can specify your own ingress configuration for the Helm deployment to make the BPDM Bridge Dummy available over Ingress. Note that you need to have the appropriate Ingress controller installed in your cluster first. For example, consider a Kubernetes cluster with an Ingress-Nginx installed. An Ingress configuration for the Bridge Dummy deployment could somehow look like this:
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTP"
hosts:
- host: business-partners.your-domain.net
paths:
- path: /bridge
pathType: Prefix
Bridge Dummy Configuration
For the default deployment you already need to overwrite the configuration properties of the application.
The Helm deployment comes with the ability to configure the BPDM Bridge Dummy application directly over the values file.
This way you are able to overwrite any configuration property of the application.properties and application-auth.properties files.
Consider that you would need to turn on auth profile first before overwriting any property in the corresponding properties file could take
effect.
Overwriting configuration properties can be useful for connecting to a remotely hosted BPDM Gate and Pool instance:
applicationConfig:
bpdm:
pool:
base-url: http://remote.domain.net/api/catena
gate:
base-url: http://remote.domain.net/api/catena
Entries in the "applicationConfig" value are written directly to a configMap that is part of the Helm deployment.
This can be a problem if you want to overwrite configuration properties with secrets.
Therefore, you can specify secret configuration values in a different Helm value applicationSecrets.
Content of this value is written in a Kubernetes secret instead.
If you want to specify a keycloak client secret for example:
applicationSecrets:
bpdm:
security:
credentials:
secret: your_client_secret
4. BPDM Cleaning Dummy
The prerequisites for running this service is same. In an existing Kubernetes cluster the application can be deployed with the following command:
helm install release_name ./charts/bpdm/bpdm-cleaning-service-dummy --namespace your_namespace -f /path/to/my_release-values.yaml
This will install a new release of the BPDM Cleaning Dummy in the given namespace.
On default values this release deploys the latest image tagged as main from the repository's GitHub Container Registry.
By giving your own values file you can configure the Helm deployment of the BPDM Cleaning Dummy freely. In the following sections you can have a look at the most important configuration options.
Image Tag
Per default, the Helm deployment references the latest BPDM Cleaning Dummy release tagged as main.
This tag follows the latest version of the Cleaning Dummy and contains the newest features and bug fixes.
You might want to switch to a more stable release tag instead for your deployment.
In your values file you can overwrite the default tag:
image:
tag: "latest"
Profiles
You can also activate Spring profiles in which the BPDM Cleaning Dummy should be run. In case you want to run the Cleaning Dummy with authorization enabled you can write the following:
springProfiles:
- auth
Ingress
You can specify your own ingress configuration for the Helm deployment to make the BPDM Cleaning Dummy available over Ingress. Note that you need to have the appropriate Ingress controller installed in your cluster first. For example, consider a Kubernetes cluster with an Ingress-Nginx installed. An Ingress configuration for the Cleaning Dummy deployment could somehow look like this:
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTP"
hosts:
- host: business-partners.your-domain.net
paths:
- path: /cleaning
pathType: Prefix
Cleaning Dummy Configuration
For the default deployment you already need to overwrite the configuration properties of the application.
The Helm deployment comes with the ability to configure the BPDM Cleaning Dummy application directly over the values file.
This way you are able to overwrite any configuration property of the application.properties and application-auth.properties files.
Consider that you would need to turn on auth profile first before overwriting any property in the corresponding properties file could take effect.
Entries in the "applicationConfig" value are written directly to a configMap that is part of the Helm deployment.
This can be a problem if you want to overwrite configuration properties with secrets.
Therefore, you can specify secret configuration values in a different Helm value applicationSecrets.
Content of this value is written in a Kubernetes secret instead.
If you want to specify a keycloak client secret for example:
applicationSecrets:
bpdm:
security:
credentials:
secret: your_client_secret
5. BPDM Orchestrator
The prerequisites for running this service is same. In an existing Kubernetes cluster the application can be deployed with the following command:
helm install release_name ./charts/bpdm/bpdm-orchestrator --namespace your_namespace -f /path/to/my_release-values.yaml
This will install a new release of the BPDM Orchestrator in the given namespace.
On default values this release deploys the latest image tagged as main from the repository's GitHub Container Registry.
By giving your own values file you can configure the Helm deployment of the BPDM Orchestrator freely. In the following sections you can have a look at the most important configuration options.
Image Tag
Per default, the Helm deployment references the latest BPDM Orchestrator release tagged as main.
This tag follows the latest version of the Orchestrator and contains the newest features and bug fixes.
You might want to switch to a more stable release tag instead for your deployment.
In your values file you can overwrite the default tag:
image:
tag: "latest"
Profiles
You can also activate Spring profiles in which the BPDM Orchestrator should be run. In case you want to run the Orchestrator with authorization enabled you can write the following:
springProfiles:
- auth
Ingress
You can specify your own ingress configuration for the Helm deployment to make the BPDM Orchestrator available over Ingress. Note that you need to have the appropriate Ingress controller installed in your cluster first. For example, consider a Kubernetes cluster with an Ingress-Nginx installed. An Ingress configuration for the Orchestrator deployment could somehow look like this:
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTP"
hosts:
- host: business-partners.your-domain.net
paths:
- path: /cleaning
pathType: Prefix
Orchestrator Configuration
For the default deployment you already need to overwrite the configuration properties of the application.
The Helm deployment comes with the ability to configure the BPDM Orchestrator application directly over the values file.
This way you are able to overwrite any configuration property of the application.properties and application-auth.properties files.
Consider that you would need to turn on auth profile first before overwriting any property in the corresponding properties file could take effect.
Entries in the "applicationConfig" value are written directly to a configMap that is part of the Helm deployment.
This can be a problem if you want to overwrite configuration properties with secrets.
Therefore, you can specify secret configuration values in a different Helm value applicationSecrets.
Content of this value is written in a Kubernetes secret instead.
If you want to specify a keycloak client secret for example:
applicationSecrets:
bpdm:
security:
credentials:
secret: your_client_secret
Stopping the cluster
stop minikube
minikube stopstop the processes used for port forwarding and minikube dashboard
shut down the Docker daemon
How to debug an application in the cluster
If you want to connect your IDE to one of the applications in the cluster, you need to enable debug mode for that application by overriding the entrypoint (using the command and args fields in the deployment resource). How to do this depends on the application. For the BPDM, as it is based on Spring Boot and Kotlin, you would need to add this flag to the start command:
-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=8000
Then you can forward the port 8000 for the BPDM deployment to your host machine and connect your IDE to that port.